1. Understanding Multi-AZ (Availability Zone) and Multi-Region
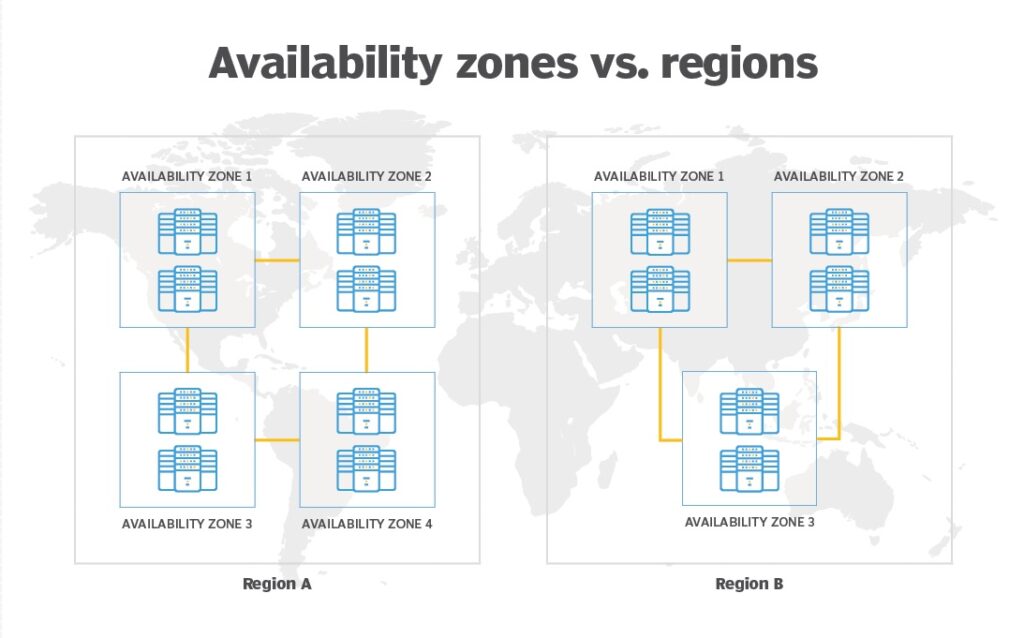
Multi-AZ (Multi-Availability Zone) refers to deploying resources and services within the same Region but across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) to ensure high availability and fault tolerance.
- Region: A specific geographical area (e.g., US-East-1).
- AZ (Availability Zone): An independent data center within a Region (e.g., Sunteco Cloud’s Eco DC).
Multi-Region involves deploying resources and services across multiple Regions, i.e., geographically independent areas. This improves resilience, optimizes latency, and ensures service stability even if an entire Region experiences an outage.
2. Differences Between Multi-Region and Multi-AZ
While both Multi-Region and Multi-AZ aim to enhance system availability and durability, they differ significantly in implementation and scope.
| Aspect | Multi-Region | Multi-AZ |
|---|---|---|
| Real-World Applications | – Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication: Data from a bucket in one Region is replicated to a bucket in another Region.<br>- Route 53 Global DNS: Resolves DNS based on geographic location to route traffic to the nearest Region.<br>- DynamoDB Global Tables: Deploys globally distributed databases. | – AWS RDS Multi-AZ Deployment: Data on an RDS instance is synchronously replicated to another AZ for high availability.<br>- EC2 Auto Scaling with Multiple AZs: Distributes instances across AZs.<br>- Load Balancer (ELB): Distributes traffic across multiple AZs. |
| Characteristics | – Regions are located in different geographical areas (e.g., US-East, AP-Southeast, EU-Central).<br>- Data and services are replicated or deployed across multiple Regions.<br>- Latency between Regions is significantly higher than between AZs. | – AZs are typically within the same geographical area but physically separated for safety.<br>- Data and services can be replicated across AZs to ensure high availability.<br>- Latency between AZs is very low (a few milliseconds). |
| Benefits | – Global Disaster Recovery: Provides backup if an entire Region fails.<br>- Reduced User Latency: Deploys services closer to users in different regions to improve access speed.<br>- Regulatory Compliance: Meets requirements for data storage in specific countries.<br>- Scalability: Expands services globally. | – High Availability: Services can failover to another AZ without interruption if one fails.<br>- Internal Disaster Recovery: Prevents data loss during AZ-specific incidents.<br>- Low Latency: Fast access due to proximity of AZs. |
| Use Cases | – Global applications like Netflix or TikTok serving users across multiple regions.<br>- Systems requiring large-scale disaster recovery.<br>- Companies with customers in multiple countries needing fast access and regulatory compliance.<br>- SaaS applications or services with high global traffic. | – Financial or banking applications requiring high availability.<br>- API systems or web services needing 24/7 uptime.<br>- Databases that must prevent data loss during incidents. |
3. Which Model Should You Choose?
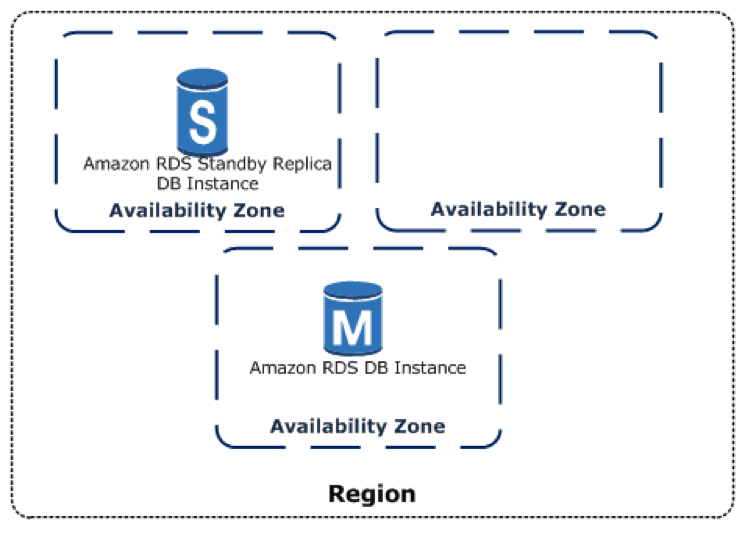
Multi-AZ consists of one or more independent data centers, each with separate power, networking, and redundant connectivity. Since Availability Zones (AZs) are physically isolated, localized incidents like fires or floods affect only a single AZ, maintaining system stability.
The Multi-AZ model is particularly suitable for systems requiring high availability within a specific region while optimizing latency and operational costs.
In contrast, Multi-Region is ideal for protecting systems against large-scale disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, or wars. However, its drawback is higher latency, making real-time data synchronization between Regions challenging and less efficient.
Thus, Multi-Region is typically chosen for globally operating systems that require disaster recovery capabilities or compliance with region-specific data storage regulations.
Globally, major cloud service providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud have robustly implemented the Multi-AZ and Multi-Region models. In Vietnam, Sunteco is a pioneer in cloud computing, adopting both models to deliver stable and flexible infrastructure to its customers.